-
What is a VR depth camera and what is it used for?
A VR depth camera is a camera designed to measure the depth of objects in a virtual or augmented reality environment. It is used for motion tracking, object recognition and other interactive applications.
-
How does a VR depth camera work?
A VR depth camera measures the depth of objects by using different technologies, such as Time-of-Flight (ToF), stereoscopic and structured light. These technologies use light signals to measure the distance between the camera and the objects to determine depth.
-
Which VR depth camera is best for gaming?
This depends on the specific requirements of the game and VR headset. Microsoft's Kinect and Stereolabs' ZED camera are popular for gaming, due to their high accuracy and speed.
-
Can a VR depth camera also be used for 3D scanning?
Yes, some VR depth cameras can also be used for 3D scanning, such as Occipital's Structure Sensor and Stereolabs' ZED camera.
-
What are some future developments for VR depth cameras?
Future developments for VR depth cameras include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve accuracy and performance, as well as the development of portable depth cameras capable of measuring depth without the need for external sensors.
All about VR Depth cameras
Virtual Reality (VR) technology has changed the way we play, learn, work and communicate. An important part of the VR experience is its ability to create an immersive sense of depth. Depth cameras are used to measure the depth of a scene and then use this Information to generate a realistic, three-dimensional representation. In this blog we take a closer look at how VR depth cameras work and their applications.
Tip: did you also know that Trackers exist? Read more about this in this blog. Sensors & Trackers
How do VR depth cameras work?
VR depth cameras work in different ways, but generally they work through Time-of-Flight (ToF) technology or stereoscopy. ToF cameras emit light to an object and then measure the time it takes for the light to bounce back to the camera. This displays the distance to the object, which can be used to calculate the depth of a scene. Stereoscopy, on the other hand, works by using two cameras that capture an image from different angles. Combining these images allows the camera to calculate the depth of a scene.
What are the applications of VR depth cameras?
Of course, one of the main applications of VR depth cameras is gaming. Measuring the depth of a scene allows game developers to create a much more realistic sense of depth, making for a more immersive experience. In addition, depth cameras can be used to track the player's movement, making the VR experience even more realistic.
But the applications of VR depth cameras go beyond gaming. For example, they can be used to create virtual tours of buildings or museums. By using a depth camera to scan a building or museum, a VR user can then take a virtual tour of the space and get a sense of depth, as if he or she were actually there. Depth cameras can also be used for medical applications, such as scanning the body to create 3D models for surgery and tracking patients' movement during rehabilitation.
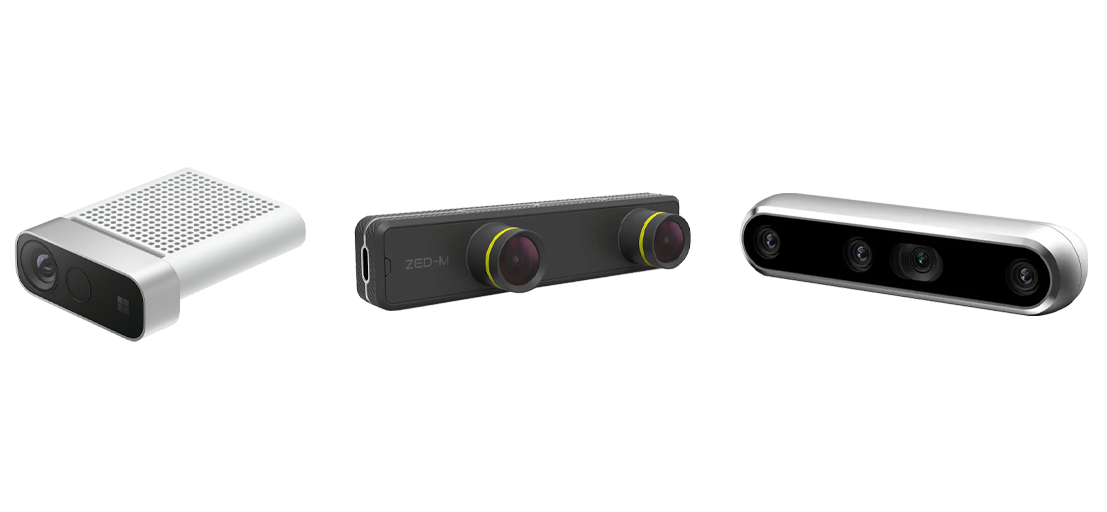
What VR depth cameras are on the market?
- Kinect: Kinect from Microsoft was originally designed as an accessory for the Xbox gaming console, but can also be used for VR applications. It uses ToF technology to measure depth and can be used for motion tracking and object recognition.
- Intel RealSense: Intel RealSense is a ToF camera designed for use in VR headsets and other AR/VR applications. It can capture depth information with with high accuracy and also provides hand and face recognition.
- ZED Camera: The Stereolabs ZED camera uses stereoscopy to measure depth information and offers high accuracy and speed. It is designed for use in AR/VR headsets and other applications where a realistic sense of depth is required.
- Structure Sensor: Occipital's Structure Sensor is a ToF camera that connects to an iPad or other mobile devices. It offers a wide range of applications, including 3D scanning and VR applications.
- Leap Motion: Leap Motion is a hand-tracking sensor that can be used in combination with with VR headsets to track the user's hand movements. It provides accurate and responsive tracking and can be used for interactive VR applications.
- Microsoft Kinect: The Microsoft Azure Kinect is another depth camera that can also be used for VR applications. It is the successor to the Kinect sensor and offers improved performance and features. The Azure Kinect uses Time-of-Flight technology to measure the depth of objects, making it suitable for applications such as motion tracking and object recognition.
What sets the Azure Kinect apart from other VR depth cameras is the ability to link multiple sensors to create a larger field of view. This can be useful for VR applications where a wide field of view is required, such as in architectural visualization or gaming. In addition, the Azure Kinect has a built-in AI processor that enables machine learning and Computer vision. This allows the device to perform more complex tasks such as detecting objects and tracking hand movements with with higher precision and reliability.

Conclusion
VR depth cameras are an important part of the VR experience. They make it possible to create realistic depth in a virtual environment and thus provide a more immersive experience for the user. The applications of this technology are versatile and range from gaming to medical applications. The further development of VR depth cameras will undoubtedly contribute to the growth of the VR industry and open up new possibilities for applications that we cannot yet imagine.
Tip: View our offer for VR Depth cameras 360 Degree & Depth Cameras
Questions or more Information about VR depth cameras?
Do you have any questions about VR depth cameras or would you like to receive more Information about this? Our specialists are happy to assist you and can tell you more about it. Please contact with our customer service via our form. Send us a message and you will receive an answer to your question or comment as soon as possible. What can we help you with?
Frequently asked questions about VR depth cameras
Learn more about this subject?
Contact with us! Our specialists are happy to help you.
Send a message Check out our other blogs